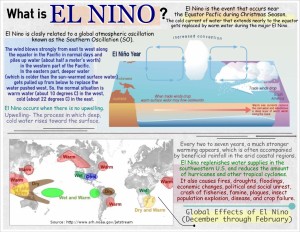
What is EL NIN0 ei the Equator ElNNino isil%tchf event hCaUsctcmuarss Season.
*The cold current of water that extends nearly to the equator
gets replaced by warm water during the major El Nino.
El Nino is closly related to a global atmospheric oscillation cOn
known as the Southern Oscillation (SO).
The wind blows strongly from east to west along
the equator in the Pacific in normal days and El Nino Year
piles up water (about half a meter’s worth) ,IVNV
in the western part of the Pacific.
In the eastern part. deeper water
(which is colder than the sun-warmed surface water)
gets pulled up from below to replace the
water pushed west. So. the normal situation is
warm water (about 10 degrees C) in the west,
cold (about 22 degrees C) in the east. warm surface Kotw may flow easlwartis
wan,: set aotenes now
El Nino occurs when there is no upwelling. • dnn aye of wine SW
Upwelling- The process in which deep, mongols om•
cold water rises toward the surface.
Every two to seven years, a much stronger
warming appears, which is often accompanied
by beneficial rainfall in the arid coastal regions.
El Nino replenishes water supplies in the
southwestern U.S. and reduces the amount
• of hurricanes and other tropical cyclones.
11R411k It also causes fires, droughts, floodings,
economic changes, political and social unrest,
Wet) crash of fisheries, famine, plagues, insect
Cet and Warm population explosion, disease, and crop failure.
Dry arid . Global Effects of El Nino
Source: http://w .srh.no ■ia.gov/jetstream (December through February)